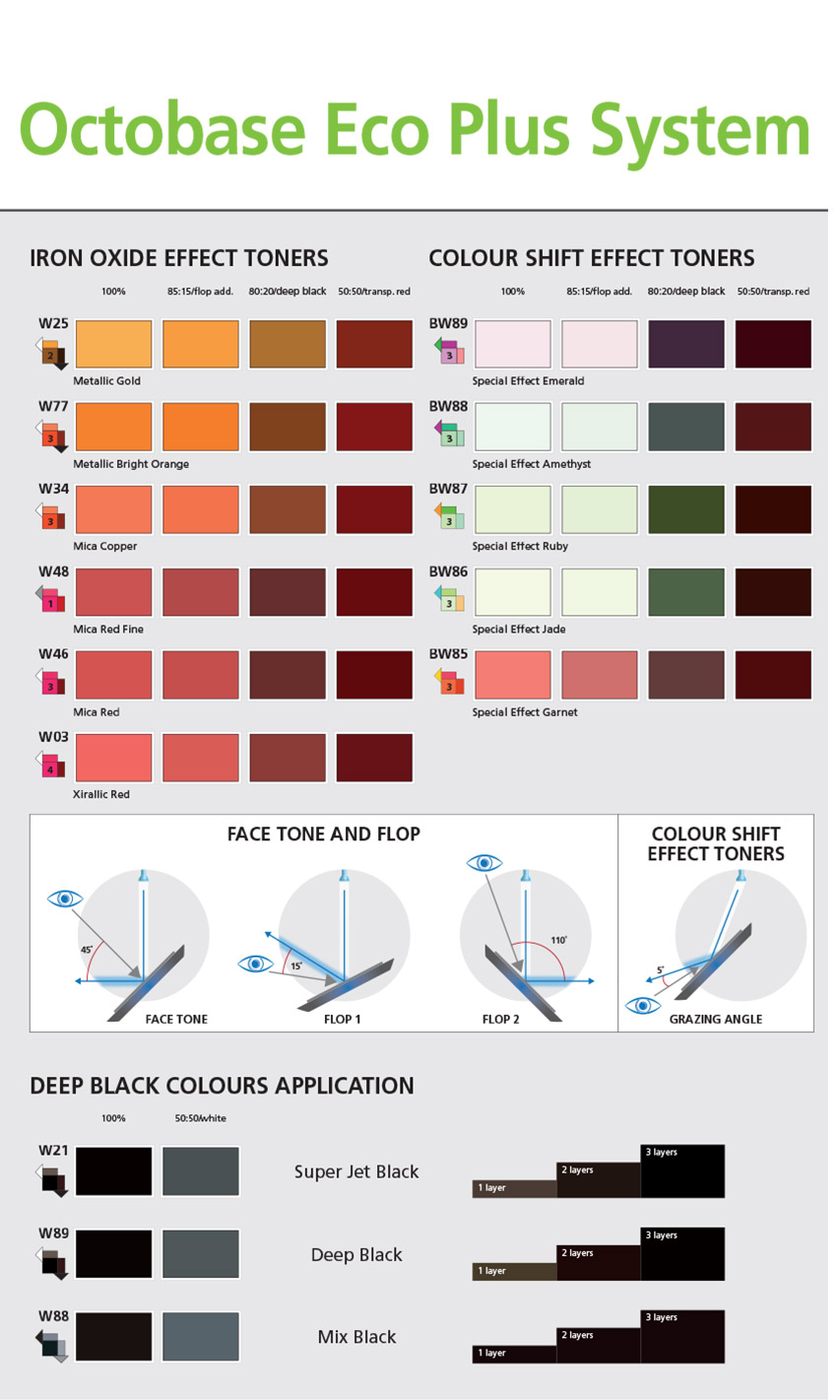
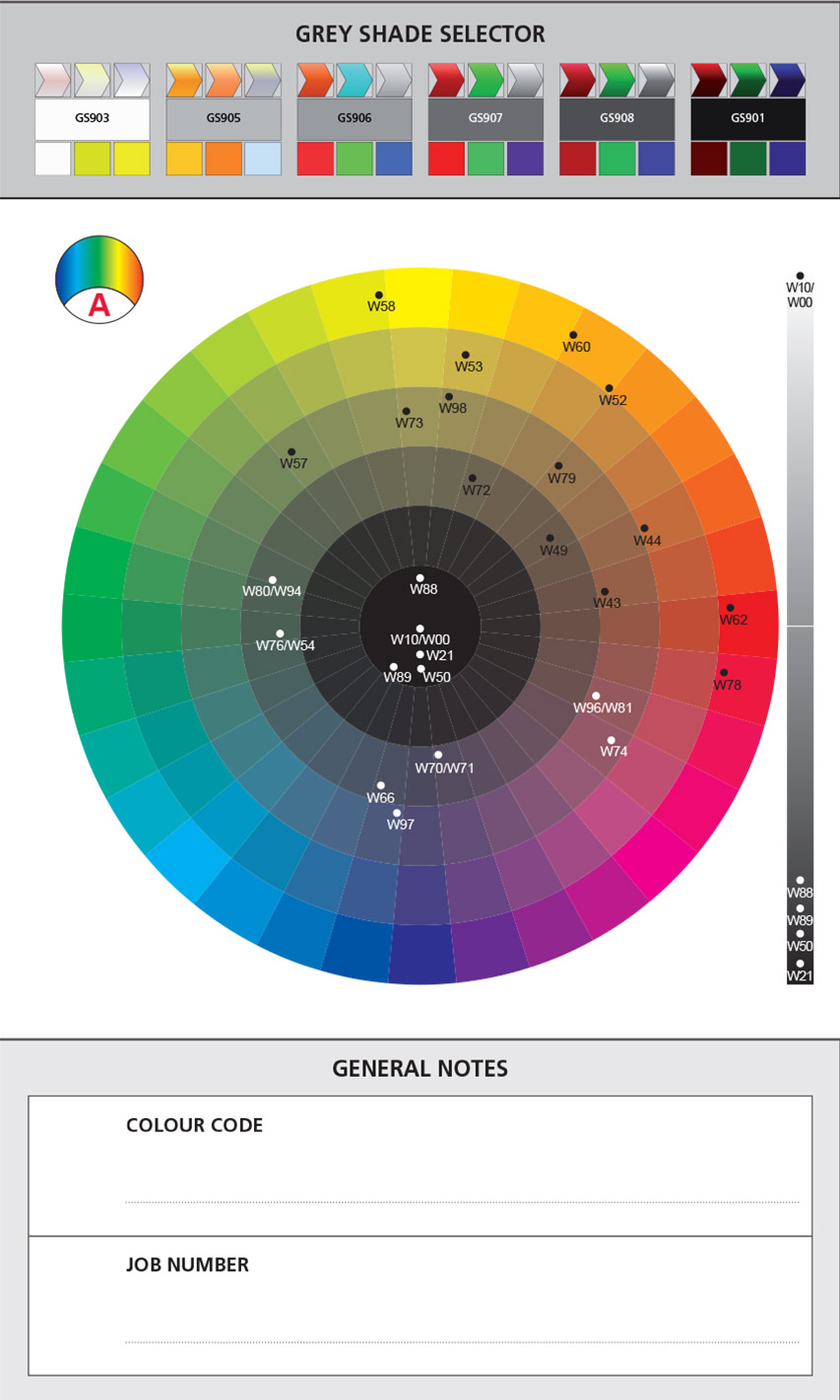
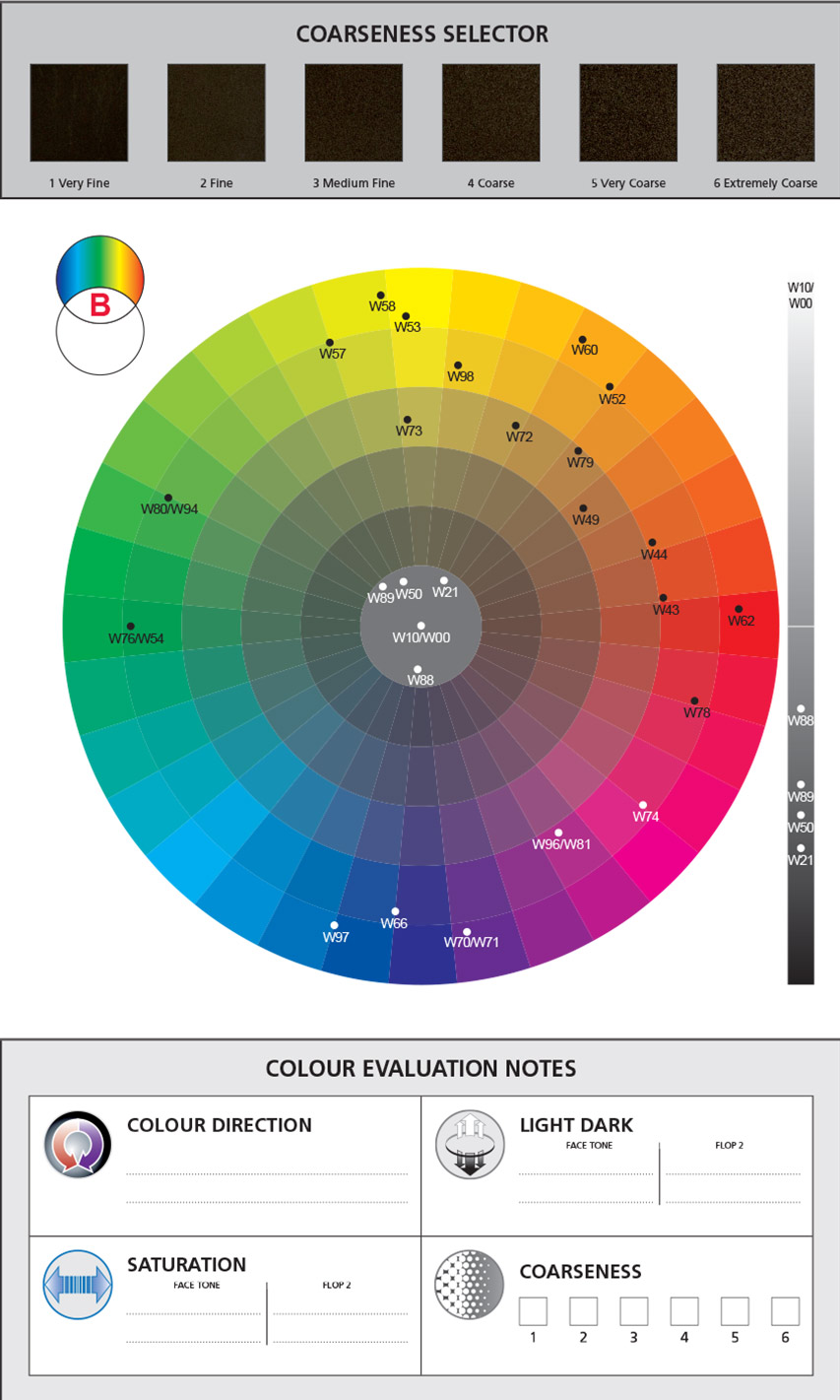
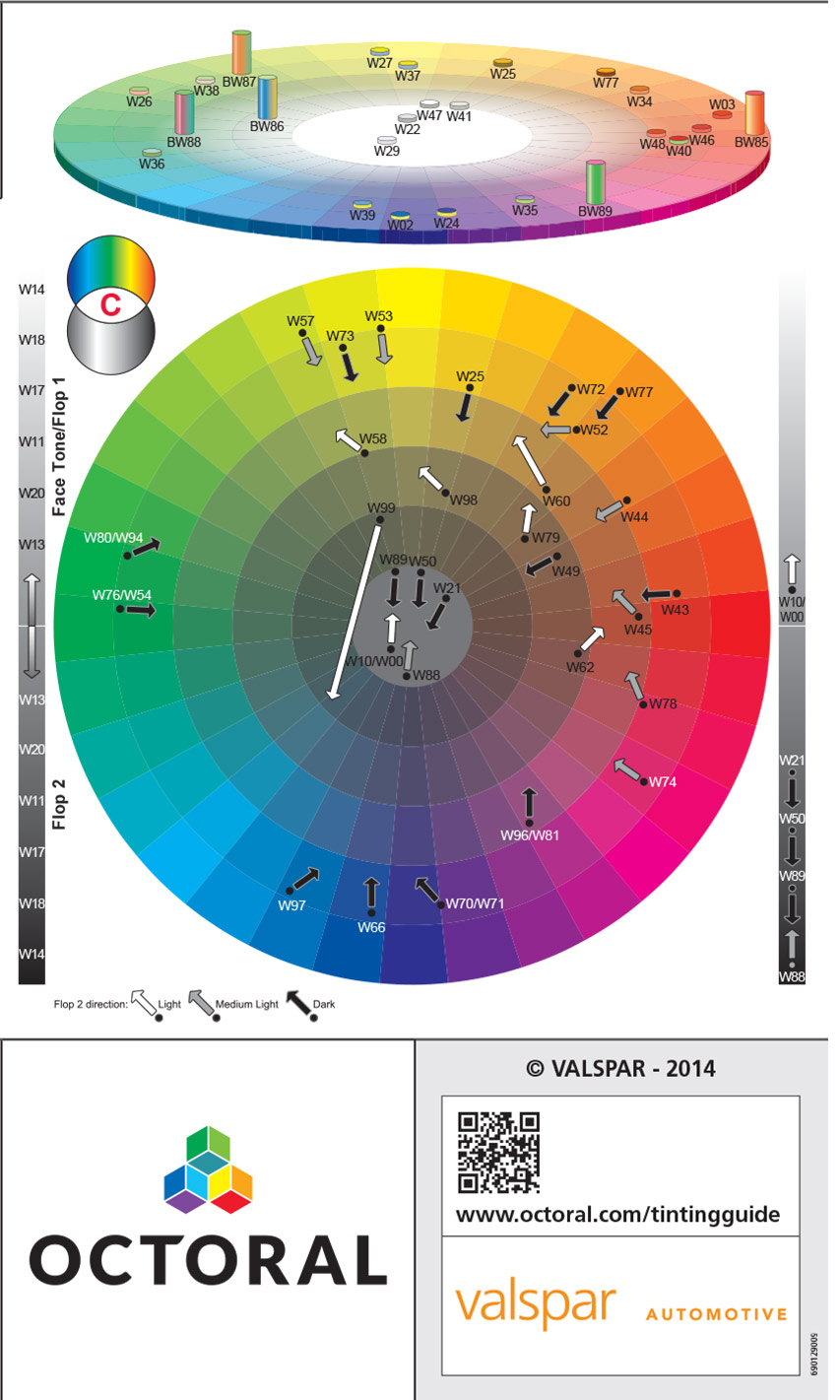
Colour Circles
Colour circle A featuring the mixing colours mixed without white:
- The mixing colours are shown on the circle at the position that corresponds with the following properties:
- colour area: the colour area that corresponds with the mixing colour
- the colour direction; more to the left or right of the colour area
- saturation (cleaner or dirtier): further from or closer to the circle's centre
- complementary colours are positioned opposite one another on the circle
- complementary colours neutralize one another after they have been mixed and produce a greyish result
Colour circle B featuring the mixing colours mixed with white:
- In principle, this is same as the first circle, but due to the mixture with white the position of the mixing colours on the circle has been adjusted.
Colour circle C featuring the mixing colours mixed with metallic:
- Same as colour circles A and B with regard to: colour, colour direction and saturation.
- In addition, flop 2 - the colour flop and depth flop - is also shown
Tilted colour circle featuring the (multi-)effect colours:
- This tilted circle (flop 1 position) features all ‘multi-effect colours’ categorised according to main colour
- The multiple colour effect of these mixing colours is indicated on the colour bar in the circle
- When mixed, the complementarily positioned colours will produce a whitish result
- This circle could be used for the purpose of adjusting the colour direction and for complementary colour shifts, but only in the case of multi-effect colours